How much is Microsoft Corp share price overvalued?
May 31, 2024
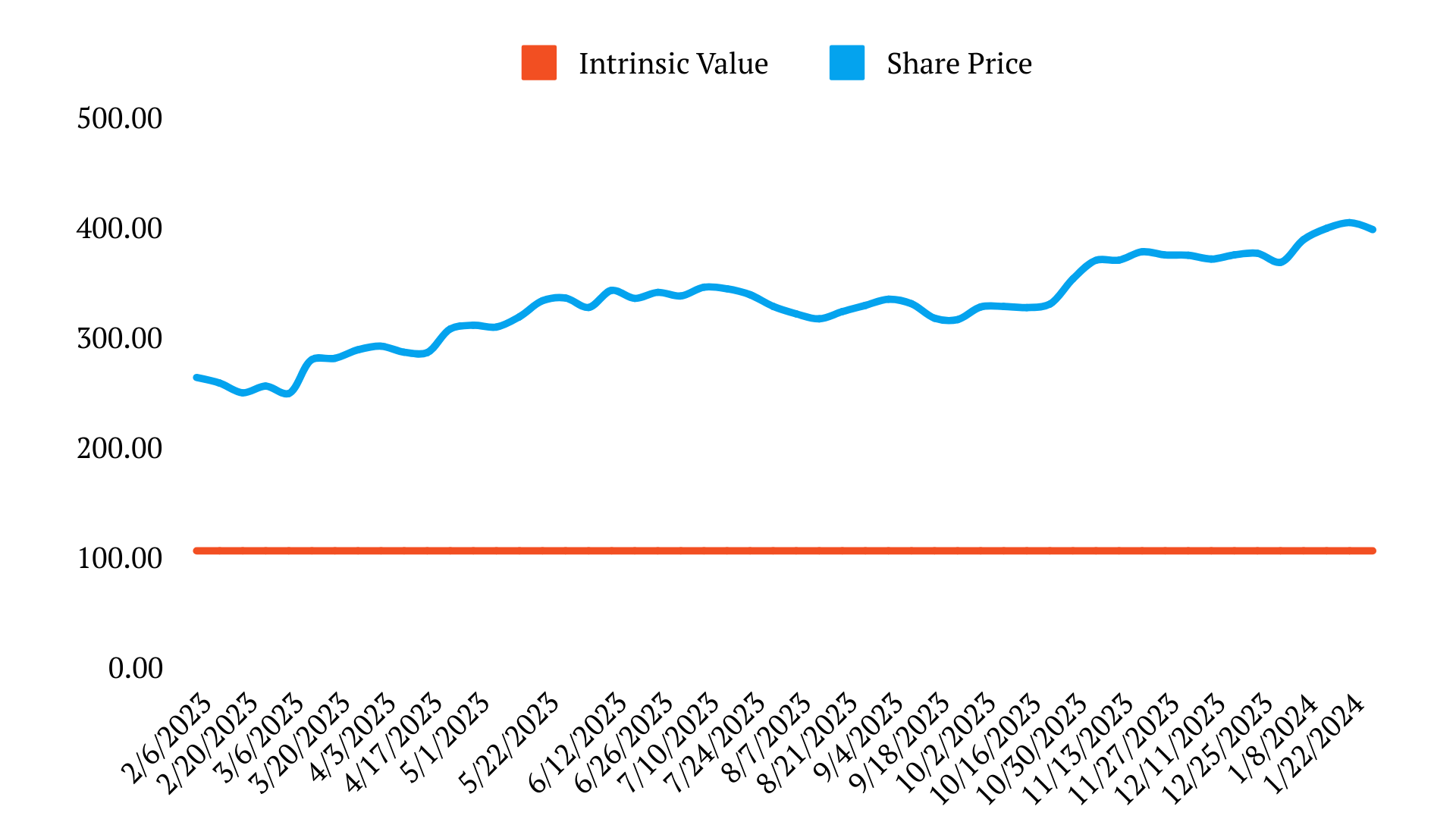

Despite the high share, you can still expect around 7.5% return on equity for every dollar invested in Microsoft.
Probably best known for its operating system, the company is a powerhouse, with incredible barriers to entry. I don’t believe that you can replicate this business, as the network effects are extreme.
Microsoft position in the market is protected by the fact that there are massive advantages for users, as everyone is using it. They make it simple to share data in the same format, like word, excel, PowerPoint and such like.
It would take enormous disruption in the market to displace it. Therefore, when the price drops, for me its always one to pick up.
Today I will value Microsoft looking at the potential growth, and our expected returns for every dollar we invest in the business. This will consist of 3 parts. Firstly, we look at the distribution yield percentage.
What percentage of the enterprise value is being distributed to the stakeholders of the business? The owners, the banks and such like. Next we look at the expected returns linked to growing the business next year maybe beyond, and the final component is the organic growth that the company will get just based on the growing economy.
So lets start with the first component, Microsoft is one of the highest value companies in the world, the market cap at the end of 2023 was sitting at 2.53 trillion dollars. If I allow for the reported debt and cash at the end of the year, this leaves us with an enterprise value of 2.47 trillion dollars.
Next we work out what percentage of this enterprise value is being distributed to stakeholders, Firstly they issued a dividend of 19.8 Bn dollars to shareholders in 2023. Then there were interest expenses of 1.968 bn that needed to be paid to the bank for existing debt, and then a net issuance of new debt of +2.7 bn dollars from financial institutions.
Microsoft also repurchased some stock from shareholders in the region of 22.245 bn dollars, and finally, there was some other financing in the region of 1bn dollars. This represents a total distribution to stakeholders of 4.7 bn dollars, or 1.93 % of the enterprise value.
The second part of our expected returns comes from the potential growth of Microsoft. So first we look at the historical returns on the invested capital. The total assets for Microsoft have grown to 411 bn dollars in 2023. However, some of these assets have been purchased not as a result of the owners’ equity and loans, but that of spontaneous liabilities. This is not invested capital – so we remove it.
For payables owed to supplier and accrued expenses, we take these off the asset value to find the next assets. For 2023, Microsoft has 389.7 bn dollars of net assets, and we need to will look at the returns on that invested capital. This is in the form of the net operating profit for the year.
For 2023 there was an impressive 71.7 bn dollars of net profit, and you can see the growth here has been astronomical over the last 10 years for the financials. If we divide that net operating profit by the net assets, we find our return on invested capital, 18.4% for 2023.
Next, we need to judge how much investment into assets is going towards growing the business, and how much is going to maintain the current operation of Microsoft to sustain the assets they already have. The capital expenditure for 2023 was 28.1 bn dollars. I have worked out that approx. 13.8 bn dollars will be used to maintain the current productive capacity of the business, and 14.2 bn dollars will be used to grow the business.
This capital expenditure is 19.86% of the net operating profit for 2023, and you can see over time , that the % of NOPAT spent on growth is rising rapidly in Microsoft - a good sign for the future.
If I multiply our percentage of net operating profit being spent on growth by the return on invested capital demonstrated previously, we arrive at expected growth of 3.66%. If we add our distribution yield to stakeholders of 1.93% to the expected growth of 3.66% to the organic growth estimated to be 1%.
We can expect total expected returns of 6.59% for every dollar invested into Microsoft. If I adjust for leverage, this increases to 7.72% for every dollar invested in Microsoft equity.
If you couple the fact that Microsoft have incredible barriers to entry and competitive advantage, if it keeps investing in its future the way it is presently, and the Returns on invested capital repeat the historical values, it is always something I pick up when there is multiple compression.
General Overview
Microsoft Corporation is a global technology company that develops, licenses, and supports a wide range of software products and services. Here’s an overview of their business:
- Founding and History:
- Founded on April 4, 1975, by Bill Gates and Paul Allen, Microsoft has played a pivotal role in shaping the technology landscape.
- Bill Gates, a Harvard College dropout, led the company during its formative years.
- Business Segments:
- Productivity and Business Processes:
- Offers tools like Microsoft Office, including Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook.
- Provides Microsoft Teams for collaboration, Office 365 Security and Compliance, and Microsoft Viva.
- Serves both enterprise and consumer markets.
- Intelligent Cloud:
- Includes Azure, Microsoft’s cloud computing platform.
- Offers server products, cloud services, and enterprise solutions.
- Acquired GitHub and Nuance to enhance its cloud offerings.
- More Personal Computing:
- Focuses on Windows operating system licensing (OEM and non-volume).
- Includes devices like Surface and HoloLens.
- Engages in gaming through Xbox hardware, content, and cloud gaming.
- Provides search and news advertising via Bing and Microsoft News
- Leadership:
- Satya Nadella, Chairman and CEO, leads Microsoft.
- Other key executives include Bradford L. Smith, Amy E. Hood, Judson B. Althoff, and Christopher David Young.
- Employee Strength:
- Microsoft has approximately 221,000 full-time employees worldwide.
- Their workforce contributes to innovation, product development, and customer support
- Impact and Reach:
- Microsoft’s software products and services are used globally by individuals, businesses, and governments.
- Their commitment to technology, cloud services, and productivity tools continues to shape the industry.
In summary, Microsoft’s diverse portfolio spans productivity tools, cloud services, operating systems, and devices. Their impact on the tech world remains significant, driven by innovation and a global presence.
PEST Analysis

Let’s explore a PESTEL analysis of Microsoft Corporation, considering the external factors that influence their business:
- Political Factors:
- Political Stability: Most markets worldwide exhibit stability, creating opportunities for Microsoft to invest and improve performance.
- Government Support for Automation: Increasing governmental support for automation allows Microsoft to enhance sales in computer technology and consumer electronics through government clients.
- International Trade Agreements: While these agreements facilitate global sales, they also pose a threat by increasing foreign firms’ competitiveness in developed countries.
- Economic Factors:
- Global Economic Conditions: Economic fluctuations impact Microsoft’s revenues and profitability.
- Consumer Spending Patterns: Economic health affects consumer spending on software, hardware, and cloud services.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations can impact Microsoft’s international operations.
- Social Factors:
- Consumer Preferences: Microsoft must adapt to changing preferences, such as cloud-based services and remote work tools.
- Digital Literacy: The company benefits from a digitally literate population that uses its products.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Social trends influence Microsoft’s workforce and corporate culture.
- Technological Factors:
- Advancements in Cloud Computing: Microsoft’s success is tied to Azure and other cloud services.
- Software Development and Innovation: Staying ahead in technology drives competitiveness.
- Cybersecurity Challenges: As technology evolves, so do security threats.
- Legal Factors:
- Intellectual Property Laws: Microsoft’s patents and copyrights are crucial for protecting its innovations.
- Antitrust Regulations: The company faces scrutiny due to its market dominance.
- Privacy and Data Protection Laws: Compliance is essential in handling user data.
- Environmental Factors:
- Sustainability Initiatives: Microsoft focuses on reducing its environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency: The company invests in energy-efficient data centers.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Environmental practices extend to suppliers.
In summary, Microsoft’s strategic decisions consider political stability, economic conditions, social trends, technological advancements, legal requirements, and environmental sustainability. These factors shape their business competitiveness and resilience.
Porters 5 Forces
Let’s analyze Microsoft Corporation using Porter’s Five Forces model, which helps assess the competitive environment in an industry:
- Competitive Rivalry:
- Strong Force: Competition is intense in the computer technology industry. Major players like Microsoft, Apple, Google, and Amazon vie for market dominance.
- Implications for Microsoft: To maintain its position, Microsoft must focus on strategies that enhance its competitive advantage. Investing in research and development, improving product development, and fostering innovation are essential.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers (Customers):
- Moderate Force: Customers have some influence due to their purchasing decisions. They can switch to alternative products or services.
- Implications for Microsoft: The company must ensure customer satisfaction, offer attractive pricing, and provide value-added services to retain buyers.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
- Moderate Force: Suppliers (e.g., hardware manufacturers, software developers) impact Microsoft’s operations. While not overly powerful, they can influence pricing and terms.
- Implications for Microsoft: Managing supplier relationships effectively and diversifying the supplier base are crucial.
- Threat of Substitutes (Substitution):
- Weak Force: There are limited direct substitutes for Microsoft’s core products (e.g., Windows OS, Office Suite, Azure). However, indirect substitutes (e.g., open-source software, cloud-based alternatives) exist.
- Implications for Microsoft: While the threat is minimal, continuous innovation and product enhancement can make Microsoft’s offerings more attractive.
- Threat of New Entrants (New Entry):
- Moderate Force: Barriers to entry exist due to established players, economies of scale, and network effects. However, disruptive technologies can alter the landscape.
- Implications for Microsoft: The company must stay agile, invest in emerging technologies, and adapt to changing market dynamics.
In summary, Microsoft faces strong competitive rivalry, moderate buyer and supplier power, weak substitution threat, and moderate new entry risk. Strategic decisions should consider these forces to maintain a strong position in the technology industry
Segment & Competition
Let’s explore Microsoft’s relevant business segments and their competitors, along with their strengths and weaknesses:
- Productivity and Business Processes:
- Microsoft Segment: This segment includes products like Microsoft Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook), Microsoft Teams, and Dynamics 365.
- Competitors:
- Google: Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) offers similar productivity tools.
- Apple: Apple’s iWork suite competes in this space.
- Strengths:
- Microsoft: Dominant brand image, positive externalities from existing products, strong alliances with other firms.
- Google: Innovations and cloud services.
- Weaknesses:
- Microsoft: Vulnerability to cybercrime, imitability of some products.
- Google: Intense competition, privacy concerns.
- Intelligent Cloud:
- Microsoft Segment: Azure, Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, is the core of this segment.
- Competitors:
- Amazon (AWS): Dominates the cloud industry.
- IBM: Also offers cloud services.
- Strengths:
- Microsoft: Azure’s growth, strategic alliances, cloud gaming (Xbox Game Pass), and Microsoft 365 on the cloud.
- Amazon: AWS market dominance.
- Weaknesses:
- Microsoft: Cybersecurity threats.
- IBM: Revenue challenges, transition to cloud.
- More Personal Computing:
- Microsoft Segment: Includes Windows operating system, Surface devices, Xbox, and related services.
- Competitors:
- Apple: Competes in hardware, mobile OS, and enterprise solutions.
- Sony: PlayStation competes with Xbox.
- Samsung: In mobile devices and consumer electronics.
- Strengths:
- Microsoft: Windows dominance, Xbox ecosystem, brand strength.
- Apple: Brand loyalty, ecosystem integration.
- Weaknesses:
- Microsoft: Low dominance in hardware products.
- Apple: Dependency on iPhone sales.
In summary, Microsoft’s strengths lie in its brand, alliances, and cloud services. However, it faces weaknesses related to cybersecurity and imitation. Competitors like Google, Amazon, Apple, and IBM keep the industry dynamic and competitive.
Value Chain

Let’s explore the value chain analysis for Microsoft Corporation, examining the various activities involved in creating value for the company and its customers:
- Inbound Logistics:
- Microsoft’s value chain begins with sourcing raw materials and components for its products. This includes hardware components for devices like Surface and data center infrastructure for Azure.
- Efficient procurement and supply chain management are crucial to ensure a steady supply of components.
- Operations:
- Microsoft’s core operations involve developing, maintaining, and improving its software products and cloud services. This includes:
- Software Development: Creating and updating operating systems (e.g., Windows), productivity tools (e.g., Office 365), and cloud platforms (e.g., Azure).
- Data Centers: Managing data centers worldwide to support cloud services.
- Research and Development: Innovating new technologies and features.
- These operations drive Microsoft’s competitive advantage and customer satisfaction.
- Outbound Logistics:
- Delivering software licenses, cloud services, and hardware products to customers globally.
- Efficient logistics ensure timely delivery and availability for end-users.
- Marketing and Sales:
- Microsoft’s marketing efforts focus on creating customer value and promoting its products. This includes advertising, promotions, and partnerships.
- Sales channels include both direct sales (e.g., enterprise contracts) and indirect sales (e.g., online stores, retail partners).
- Microsoft’s strong brand image and customer relationships contribute to successful marketing and sales efforts.
- Service:
- Microsoft provides value through customer service, technical support, and ongoing updates.
- Services include:
- Customer Support: Assisting users with software issues.
- Cloud Support: Helping organizations optimize their use of Azure and other cloud services.
- Security Services: Protecting customers from cyber threats.
- High-quality service enhances customer loyalty and satisfaction.
- Procurement:
- Procuring components, licenses, and intellectual property rights.
- Managing relationships with suppliers and negotiating favorable terms.
- Ensuring quality and reliability of components and services.
- Technology and Infrastructure:
- Microsoft invests heavily in technology:
- Cloud Infrastructure: Data centers, networking, and security.
- Software Development Tools: Supporting efficient coding and testing.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing products and services.
- Infrastructure includes data centers, networks, and development environments.
- Human Resources:
- Microsoft’s skilled workforce contributes to innovation, product development, and customer support.
- Training, development, and employee well-being are essential aspects.
- Diversity and inclusion initiatives promote a positive work environment.
- Firm Infrastructure and Governance:
- Leadership, governance structure, and ethical practices impact Microsoft’s overall value creation.
- Responsible marketing, business ethics, and data security are part of their firm infrastructure.
In summary, Microsoft’s value chain encompasses sourcing, software development, logistics, marketing, service, procurement, technology, human resources, and governance. Each stage contributes to their success in the technology industry.