Should we buy AutoZone, when it is in negative Equity?
Jun 02, 2024
Earnings Power Value Calculation
Would we ever invest in a company that has negative equity? AutoZone owes more money than its assets can cover, and even if they liquidated all their assets today, they would not be able to pay off the debts.
So how do we value a business like that?
Well obviously, I cannot value the business based on the assets that the company owns. So we should try and value the business on the cash flows that it will bring in over the life time of the company, and allow for the debt to be serviced in that calculation. I will use the earnings power value.
Here we focus on the profit and loss account. For AutoZone, all the numbers are heading in the right direction. Revenue, Gross profit, operating profit and the Net operating profit after tax has grown year after year like clockwork, but we want to focus on the net operating profit after tax.
Let’s take the AutoZone Net profit after tax for 2023 – 2.772 bn dollars. Let’s imagine that the continue to make that net operating profit after tax for the whole life of the company, so there would be no further growth. So, it’s a cautious approach some would say, but I would say practical approach.
Now let’s discount those future cash flows over the lifetime of the company, and then add them all together. This tells us is we continue to have sustainable earnings over the lifetime of AutoZone. This would be the cash inflow for the owners in total.
This equates to just over 45 billion dollars for AutoZone, but we also know they owe a lot, as they are in negative equity. So, let’s add back the cash, and minus the 10.9 bn dollars of debt.
We get to an earnings power value of the equity valuation of 34.362 bn dollars. Then we divide that figure by the shares outstanding, and I get to a share price of 1856.43. This is a baseline.
Growth Valuation
Their returns on invested capital are far higher than the cost of that capital, so I think it may be prudent to look at growth also for AutoZone. Every time they spend money on assets, they are getting positive returns relative to that investment.
We want to understand what kind of returns AutoZone will achieve if they invest into the business. We do this by looking at the historical invested capital and the returns on that invested capital. Let’s take the assets for AutoZone for the last 10 years. They have grown substantially like the revenue and profitability to land at 15.985 bn dollars for 2023. However, some of these assets was not bought with invested capital from owners, but with spontaneous liabilities that are owed to suppliers.
We remove them from the calculation to land on a net asset position of 8.281 bn dollars for AutoZone. Next we look at the net operating profit after tax, and by 2023, the net operating profit after tax has reached 2.772 bn dollars, again growing year on year. Now if we divide that figure by the net assets we just calculated, we reach a return on invested capital of 33.48% for the year 2023. This is phenomenal, if we ignore the negative equity issue.
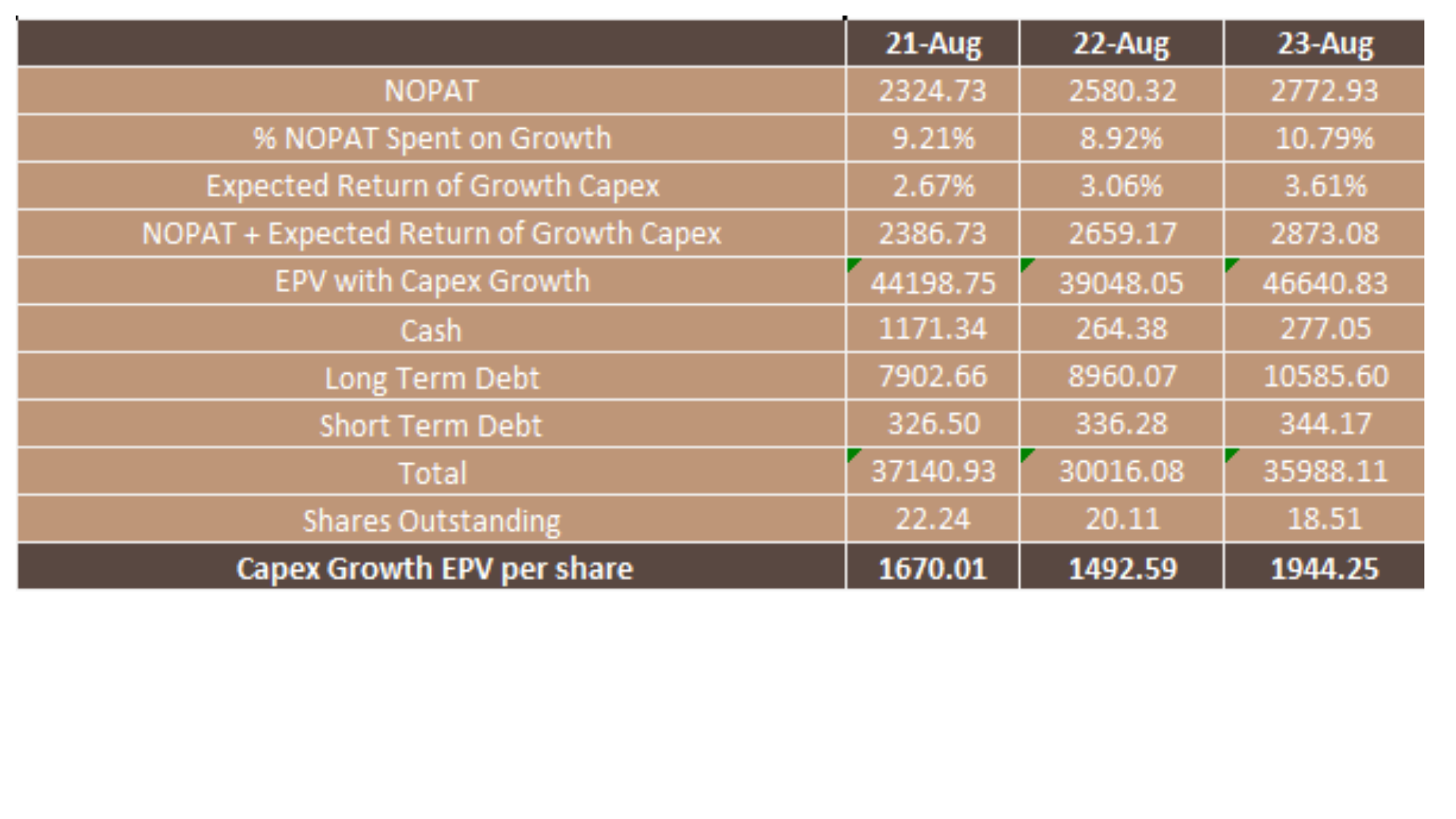
So, we know that AutoZone has returns on the invested capital of 33.48%, Now we need to understand how much AutoZone are investing for the future They tell us there capex for 2023, 796 m dollars, and I have estimated that 479 million dollars would be spent on maintaining the productive capacity that exists today, and 299 m dollar will be spent on growth.
That 299m dollars represents about 10.79 % of net operating profit. So we can expect 10.79% of NOPAT spent on growth and we know that the historical return on invested capital is 33.48% Multiply the two together and we can expect growth in Net operating profit after tax of 3.61%.
This would change our net operating profit after tax from 2.772 bn dollar in 2023 to 2.873 bn dollars in 2024 and beyond. Again, we assume that NOPAT over the lifetime of the business, and we land on 46.640 bn dollars.
Once again, we subtract the debt of 10.5 billion dollars and divide by the shares outstanding, which leaves us with a share price of 1944.25. So, our range moves from a share price of 1856.43 to 1944.25 for AutoZone.
For me to be interested, I would want the share price to be in this range. Then I can get the extra growth for free over the lifetime of the company.
General Overview
AutoZone is a prominent retailer and distributor of automotive replacement parts and accessories. Here’s an overview of their business:
- Retail Stores: AutoZone operates more than 6,000 stores across the United States, Mexico, Brazil, and Puerto Rico. Each store carries an extensive line of products for cars, sport utility vehicles, vans, and light trucks. These products include both new and remanufactured hard parts, as well as maintenance items.
- Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) Initiatives:
- AutoZone is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. They have set short-term and medium-term goals to decrease energy-related emissions by 15% by 2025 and reduce GHG emissions across the entire enterprise by 50% by 2030, measured against a 2019 baseline. Their long-term aspiration is to achieve net-zero GHG emissions across Scopes 1 and 2 by 2050.
- Community Engagement: Guided by their values, AutoZone strives to create a welcoming and diverse environment for both customers and employees. They actively engage in community initiatives and go the extra mile to support the communities where they operate.
PEST Analysis

Let’s delve into a PESTEL analysis for AutoZone, considering the macro-environmental factors that impact their business:
- Political Factors:
- Government resource allocation and time scale: The United States’ new government policies can influence investment sentiment in the Consumer Cyclical sector. Given the wider acceptance of these suggested policies among the population, it’s safe to assume that their time scale will extend beyond the mandated term of the present United States government.
- Stakeholder collaboration: non-government organizations, protest groups, and activist movements play a critical role in policymaking in the United States. AutoZone should closely collaborate with these organizations to contribute both to community goals and corporate objectives.
- Importance of local governments: Unlike in most other countries, local governments significantly impact policymaking and regulations in the United States. AutoZone must closely follow the states and territories where it operates rather than devising nationwide policies.
- Economic Factors:
- Consumer spending behavior: Economic fluctuations directly affect consumer spending patterns. AutoZone’s performance is tied to the overall economic health and disposable income of its customer base.
- Regulatory framework: Changes in economic policies, tax regulations, and trade agreements can impact AutoZone’s operations and profitability.
- Social Factors:
- Collective social trends: AutoZone needs to adapt to changing consumer preferences, such as increased interest in electric vehicles, sustainability, and convenience.
- Environmental activism: Growing awareness of environmental issues influences consumer choices. AutoZone should consider sustainable practices and eco-friendly products.
- Technological Factors:
- Technological changes: AutoZone must stay abreast of advancements in automotive technology, e-commerce, and supply chain management.
- Digital transformation: The shift toward online sales and digital customer experiences affects AutoZone’s business model.
- Environmental Factors:
- Regulatory framework for environmental factors: AutoZone operates in an environment where environmental regulations are becoming more stringent. Compliance and sustainability efforts are crucial.
- Green initiatives: AutoZone can explore eco-friendly practices, such as recycling programs and energy-efficient operations.
- Legal Factors:
- Ever-evolving legal system: AutoZone must navigate legal complexities related to intellectual property, labor laws, and consumer protection.
- Product liability: Legal risks associated with product defects or safety issues can impact AutoZone’s reputation and financial stability.
In summary, AutoZone operates in a dynamic environment influenced by government decisions, social trends, economic shifts, technological advancements, environmental concerns, and legal developments. Analyzing these factors helps AutoZone make informed strategic decisions.
Porters 5 Forces
Let’s analyze AutoZone using Porter’s Five Forces model, which helps assess the competitive environment in an industry. These five forces shape every industry and influence a company’s long-term success.
- Competitive Rivalry:
- AutoZone operates in the automotive retail sector, which is highly competitive. Major players like AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts, and O’Reilly Auto Parts vie for market share.
- Companies often engage in price wars, marketing campaigns, and product differentiation to gain an edge. The intense rivalry can impact profit margins and customer loyalty.
- Supplier Power:
- AutoZone relies on suppliers for automotive replacement parts. When suppliers have significant control, they can dictate terms and prices.
- Diversifying the supplier base is crucial to reduce dependency and maintain a competitive edge. AutoZone must manage supplier relationships effectively.
- Buyer Power:
- AutoZone’s customers (individuals, mechanics, and repair shops) have bargaining power. They can switch to competitors based on price, quality, or convenience.
- AutoZone’s customer service, product availability, and pricing strategies play a vital role in retaining buyers.
- Threat of Substitution:
- The threat of substitution exists due to alternative options for automotive parts. Customers can choose between OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts, aftermarket parts, or even online retailers.
- AutoZone must continuously improve its offerings to prevent customers from switching to substitutes.
- Threat of New Entrants:
- The automotive retail industry has moderate barriers to entry. New entrants need capital, distribution networks, and brand recognition.
- Established players like AutoZone benefit from economies of scale, customer trust, and existing infrastructure. However, disruptive technologies (e.g., electric vehicles) can alter the landscape.
In summary, AutoZone faces intense competition, supplier dynamics, buyer preferences, substitution risks, and potential new entrants. Strategic decisions should consider these forces to maintain a strong position in the market.
Segment & Competition
Let’s explore some of AutoZone’s key competitors in the automotive retail industry and analyze their strengths and weaknesses:
- Advance Auto Parts:
- Strengths:
- Strong Brand Presence: Advance Auto Parts has a well-established brand and a loyal customer base.
- Extensive Store Network: They operate over 4,800 stores across the United States, providing convenient access to automotive parts.
- Robust E-Commerce Platform: Advance Auto Parts has invested in its online presence, making it easy for customers to shop online.
- Weaknesses:
- Profit Margins: The company faces pressure on profit margins due to intense competition and pricing strategies.
- Inventory Management: Managing inventory efficiently across a large store network can be challenging.
- Market Share: While they are a major player, they still trail behind AutoZone in terms of market share.
- O’Reilly Auto Parts:
- Strengths:
- Customer Service: O’Reilly is known for excellent customer service and knowledgeable staff.
- Growing Store Count: They continue to expand their store network, reaching more customers.
- Strong Financial Performance: O’Reilly consistently reports solid financial results.
- Weaknesses:
- Regional Concentration: Their stores are primarily concentrated in certain regions, limiting nationwide coverage.
- Online Presence: While they’ve improved their e-commerce platform, it’s not as robust as some competitors.
- Competition from AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts: O’Reilly faces stiff competition from both AutoZone and Advance Auto Parts.
- NAPA Auto Parts:
- Strengths:
- Wide Product Range: NAPA offers a comprehensive range of automotive parts and accessories.
- Strong Distribution Network: Their distribution centers ensure timely availability of parts.
- Professional Customers: NAPA serves both retail customers and professional mechanics.
- Weaknesses:
- Limited Retail Presence: NAPA’s retail footprint is smaller compared to AutoZone and others.
- Brand Awareness: While well-known among professionals, NAPA may not have the same brand recognition as AutoZone.
- Online Sales: Their online sales channel needs improvement.
- Pep Boys (Manny, Moe & Jack):
- Strengths:
- Full-Service Approach: Pep Boys offers not only parts but also services like oil changes, tire rotations, and repairs.
- Tire Business: They have a strong presence in the tire market.
- Loyalty Program: Pep Boys’ loyalty program encourages repeat business.
- Weaknesses:
- Financial Challenges: The company has faced financial difficulties in recent years.
- Store Closures: Pep Boys has closed some underperforming stores.
- Competition from Specialized Retailers: They compete with specialized tire and repair shops.
In summary, each competitor has its unique strengths and weaknesses. AutoZone remains a dominant player due to its extensive store network, customer-centric approach, and commitment to quality products. However, the competitive landscape continues to evolve, and these companies adapt to stay relevant.
Value Chain
Let’s delve into a value chain analysis for AutoZone, examining the various activities involved in creating value for the company and its customers:
- Inbound Logistics:
- AutoZone’s value chain begins with sourcing automotive parts and accessories from suppliers. Efficient procurement and inventory management are critical to ensure a steady supply of products to their stores.
- Operations:
- AutoZone’s core operations involve managing its extensive network of retail stores. This includes store layout, inventory management, and customer service.
- They also handle remanufacturing processes for certain parts, ensuring quality and availability.
- Outbound Logistics:
- AutoZone’s distribution centers play a crucial role in delivering products to individual stores. Efficient logistics ensure timely restocking and availability for customers.
- Their online sales channel also relies on effective outbound logistics.
- Marketing and Sales:
- AutoZone’s marketing efforts focus on creating customer value. They engage in advertising, promotions, and loyalty programs.
- Their sales strategy involves both in-store and online channels, emphasizing customer satisfaction and convenience.
- Service:
- AutoZone provides value through customer service, technical assistance, and product knowledge. Their staff helps customers find the right parts and offers guidance on installation and maintenance.
- Services like battery testing, loaner tools, and repair guides enhance the overall customer experience.
- Procurement:
- AutoZone procures parts from suppliers globally. Negotiating favorable terms, maintaining strong relationships, and ensuring quality are essential in this stage.
- Technology and Infrastructure:
- AutoZone invests in technology for inventory management, point-of-sale systems, and e-commerce platforms.
- Their infrastructure includes distribution centers, stores, and an efficient supply chain.
- Human Resources:
- AutoZone’s skilled workforce contributes to customer satisfaction. Training, development, and employee well-being are vital aspects.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives also play a role in their value chain.
- Firm Infrastructure and Governance:
- AutoZone’s leadership, governance structure, and ethical practices impact their overall value creation.
- Responsible marketing, business ethics, and data security are part of their firm infrastructure.
In summary, AutoZone’s value chain encompasses sourcing, operations, logistics, marketing, service, procurement, technology, human resources, and governance. Each stage contributes to their success in the automotive retail industry.